Part of a series of case studies that exemplify elements of the Universal Circular Economy Policy Goals (2021) in practice.
China has adopted the circular economy as a national priority since the late 2000s and defined vehicle remanufacturing as a strategic sector.
Remanufacturing uses approximately 60% less energy and 70% fewer materials than making new products. Vehicle remanufacturing in particular has a huge market potential in China, with its existing stock of 365 million vehicles, and an automotive repairrepairOperation by which a faulty or broken product or component is returned back to a usable state to fulfil its intended use. and maintenance market worth 1 RMB trillion (USD 157 billion) annually.
Over the last decade, three key policies have propelled the growth of the vehicle remanufacturing sector in China:
Financial incentives: subsidies for enterprises that collect vehicles and component parts has increased collection rates, while consumers can avail of a 10% discount on remanufactured parts.
Industrial clusters: After a series of pilots to test the market, the State Council announced a target of 100 industrial zones that enable enterprises to exchange information and best practises;
Funding for technological advancement and standards: The Smart Remanufacturing Action Plan (2018-2020) provides funding for skills development and R&D, and introduced a standard that guaranteed functionality and quality of remanufactured parts.
Policy background
China has adopted the circular economycircular economyA systems solution framework that tackles global challenges like climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution. It is based on three principles, driven by design: eliminate waste and pollution, circulate products and materials (at their highest value), and regenerate nature. as a national priority since the late 2000s, recognising it as a means of generating growth that is decoupled from resource use. Since then, a series of dedicated remanufacturing policies have been introduced that sit within the circular economy strategic priority. This case study explores three of these policies that have led to significant growth in the vehicle remanufacturing sector.
1. Financial and regulatory incentives to increase collection rates
Swap the Old for Remanufacturing, a 2013 policy from the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the Ministry of Finance, increased collection of scrapped vehicles by around 5% by 2016. The policy provides subsidies to enterprises that collect end-of-life vehicles - both entire vehicles and component parts - as well as machines and machine tools, for remanufacturing. It also incentivises customers to buy remanufactured products by offering a 10% discount compared to buying new. Retailers can claim this back directly from the government.
In 2019, following industry feedback, the Regulation on Scrapped Vehicles was revised to expand the range of parts that could be recovered and sold from scrapped vehicles.These changes created a stronger enabling environment, expanding the scale of industrial remanufacturing and achieving a higher rate of end-of-life vehicle recovery.
2. Pilot programmes and industrial clusters to promote best practice and foster activity
Starting in the early 2010s, the Chinese government implemented a range of pilot projects to test the market potential for vehicle remanufacturing and find ways to support the sector. For example, in 2014 the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) announced a list of 20 pilot enterprises licensed to sell remanufactured products - with strict requirements on scale of production, management systems, and repair skills - which encouraged other small- and medium-sized businesses into the sector. By 2016 there were 76 pilot companies in operation, and rising interest in remanufacturing led to the State Council announcing in 2015 a target of more than 100 industrial zones.
3. Public funding to support technological advancement and standards
Remanufacturing requires expertise and advanced technology systems. In 2017 MIIT issued its Smart Remanufacturing Action Plan (2018-2020) to facilitate breakthroughs in key technologies such as disassembly, damage detection, and forming processes. It also supported the establishment of 100 high-tech enterprises, R&D centres, service centres, information platforms and industry clusters to scale remanufacturing activities in China. Crucially, MIIT also issued an official certificate for approved remanufactured products under this policy, which guarantees their functionality and quality is equal to or better than the new original products.

Lessons learned:
Setting remanufacturing as a strategic sector of the economy
In line with its vision for a circular economy, the Chinese government defined vehicle remanufacturing as a strategic sector to achieve resource circulation and reduce pollution. This has led to the development of an enabling policy framework for the industry, which has in turn provided the conditions and momentum for the industry to grow.
Providing incentives to create material loops
By providing subsidies for the collection of scrapped vehicles, through Swap the Old for Remanufacturing, the government created financial incentives for companies to keep vehicles and their materials in use. By encouraging customers to buy remanufactured products at a 10% discount, the subsidies have also promoted the establishment of a secondary market. The establishment of green industrial parks created valuable industry clusters that supported growth in remanufacturing activities.
Fostering collaboration among key actors
The NDRC, the State Council, MIIT, and the Ministry of Finance (MOF) have all been involved in the evolution of policies to develop and grow the vehicle remanufacturing industry. Interventions from different ministries have supported different elements of the industry such as technological advancement and collection of scrapped vehicles. In addition, the government engaged a range of stakeholders on policy developments, co-creating the necessary skills and legislatory backdrop for success.
Illustrating the Universal Circular Economy Policy Goals
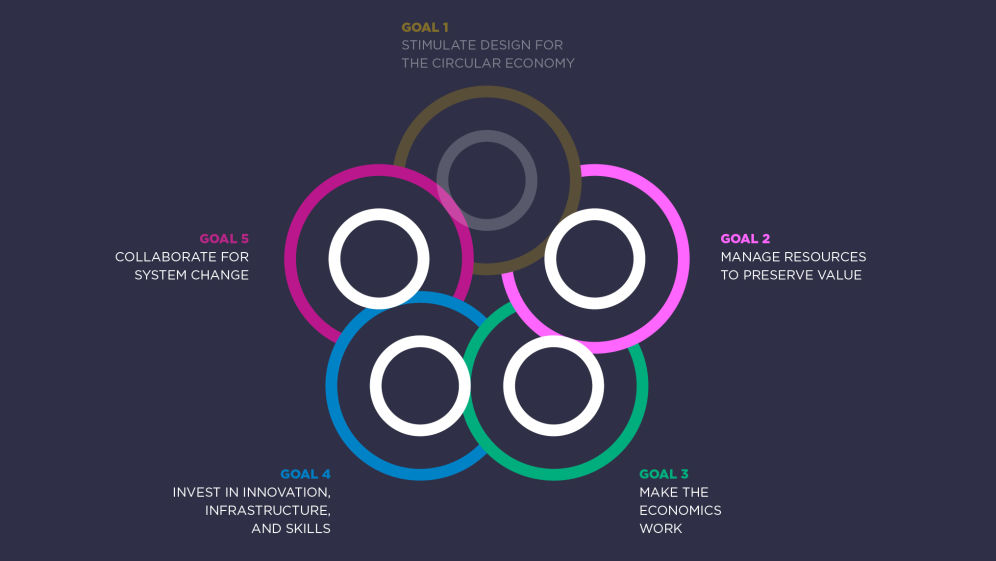
Part of a series of case studies that exemplify elements of the Universal Circular Economy Policy Goals (2021) in practice.
Download
Advancing vehicle remanufacturing in China is available in: English